This workshop example shows how to set up and run the simulation of a heavy fluid (water) droplet falling past a wedge obstacle. The lighter fluid filling the domain is paraffin.
The task is to simulate the velocity field and water volume fraction distributions.
The geometry is shown in the figure below.

The two-dimensional domain is 0.01m in all three directions. The initial bubble diameter is 0.002m. Gravity acts in the -Y direction.
From the system level:
To enter the PHOENICS-VR environment, click on the PHOENICS icon on the desktop, or click on Start, programs, PHOENICS, PHOENICS.
In PHOENICS-VR environment,
Start with an 'empty' case - click on 'File' then on 'Start New Case', then on 'Core', then click on 'OK'; to confirm the resetting.
To enter VR Editor:
This is the default mode of operation .
Set the domain size and time steps:
Click on 'Menu' (Main Menu) on the VRE-Editor panel; and set 'Droplet falling over wedge - VOF' as the Title.
Click on 'Geometry'.
Change 'Steady' to 'Transient'
Click 'Time step settings' button and set
Time at the end of last step to 1 s
Last step number to 500
Click on 'Apply' and 'OK'.
Change the x-domain size to 0.01.
Change the y-domain size to 0.01.
Change the z-domain size to 0.01.
Click on 'OK' to close the Grid mesh settings dialog.
Click on 'OK' to exit from 'Menu'.
Click on 'Reset', 'View +Z', 'Up +Y' ,then 'Fit to window'/'OK'.
Activate the solution settings for velocities and mass fraction of water:
Click on 'Models'
Leave 'Solution for velocities and pressure' to ON.
Click on 'Turbulence models' and select 'Laminar'/'OK'.
Click on Free-Surface models; and then choose VOF - CICSAM.
Leave settings for cut-off values for interface sharpening as default 0.001 and 0.999.
Leave the surface tension as 0.0.
Specify properties
Click on 'Properties'.
Set the 'Light fluid' to '59 Paraffin Oil' and the 'Heavy fluid' to '67 water'.
Click on Property 'Storage' and set 'ON' for Density and Viscosity, then on 'Previous panel'.
Keep the default setting for Domain initially full of: Light fluid
Sources settings
Click on 'Sources'
Set 'Gravitational forces' ON and click 'OK'.
Set 'Buoyancy model' to CONSTANT
Change 'Gravitational acceleration' to 0.0 in X and Z directions and -9.81 in Y.
Create the internal surfaces of the domain:
Click on 'Domain Faces'.
Set 'Wall' to 'Yes' for the Xmin, Xmax, and Ymin faces. Set 'Open' to 'Tes' for the Ymax face.
Click on 'OK' to close the Domain Faces Dialogue Box, and 'OK' again to close the reminder to set / check boundary conditions.
Numerical settings
Click on 'Numerics'.
Set 'Total number of iterations' to 60.
Click 'Previous panel'
Output settings
Click Field dump settings button and set 'Intermediate field dumps' to ON, 'Step frequency' to 20 and select a letter, say 'N' for ;Start letter for solution file'.
Click 'Previous panel', and then on 'Top menu' and 'OK' to exit from 'Menu'.
Create the WATER object:
Click on 'Settings', 'New', 'New Object', 'Blockage'.
Change name to WATER.
Click on 'Size' and set SIZE of object as:
Xsize: 0.002
Ysize: 0.002
Zsize: 'To end'
Click on 'Place' and set POSITION of object as:
Xpos: 0.004
Ypos: 0.006
Zpos: 0.0
Click on 'General', then 'Attributes'.
Define Type: 'Heavy fluid'.
Click on 'Shape', then browse to public\Basic_Shapes and select 'cylinder' for the Geometry.
Click on 'OK' to close the Attributes menu,
and on 'OK' in the Object Specification Dialogue Box.
Create the first WEDGE object:
Click on 'Settings', 'New', 'New Object', 'Blockage'.
Change name to WEDGE1.
Click on 'Size' and set SIZE of object as:
Xsize: 0.001
Ysize: 0.004
Zsize: 'To end'
Click on 'Place' and set POSITION of object as:
Xpos: 0.005
Ypos: 0.004
Zpos: 0.0
Click on 'Shape', then browse to public\Basic_Shapes and select 'wedge' for the Geometry.
The wedge will be oriented incorrectly - we must flip it through the various rotations until it is correct.
Click 'Options', 'Rotation options' the increase 'Rotate object face' until the wedge looks as expected. This will happen at position 9.
Click on 'OK' twice to exit the Object Dialogue Box.
Create the second WEDGE object:
Click on 'Settings', 'New', 'New Object', 'Blockage'.
Change name to WEDGE2.
Click on 'Size' and set SIZE of object as:
Xsize: 0.001
Ysize: 0.004
Zsize: 'To end'
Click on 'Place' and set POSITION of object as:
Xpos: 0.004
Ypos: 0.004
Zpos: 0.0
Click on 'Shape', then browse to public\Basic_Shapes and select 'wedge' for the Geometry.
The wedge will be oriented incorrectly - we must flip it through the various rotations until it is correct.
Click 'Options', 'Rotation options' the increase 'Rotate object face' until the wedge looks as expected. This will happen at position 18.
Click on 'OK' twice to exit the Object Dialogue Box.
Setting the Probe Location
Before running the solver,it is a good idea to place the probe in a suitable place to monitor the convergence of the solution. Too close to an inlet, and the value will settle down very quickly before the rest of the solution. Placed in a recirculation zone, it may still show traces of change even though the bulk solution is converged. In this case, somewhere downstream of the step is fine.
Click on the probe icon
on the toolbar or double-click the probe itself, and move the probe to X=0.005, Y=0.003, Z=0.005
Setting the Grid
Click the mesh toggle
to display the grid. The orange lines are region boundaries, located at the edges of the objects. The blue lines are 'ordinary' grid lines inserted by the auto-mesher. In this case, the default grid in X (52 cells) and Y (55 cells) is adequate.
In the PHOENICS-VR environment, click on 'Run', 'Solver'(Earth), and click on 'Yes' to confirm the action.
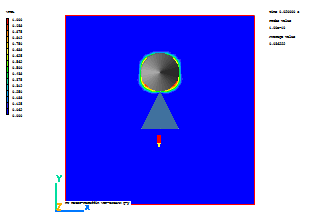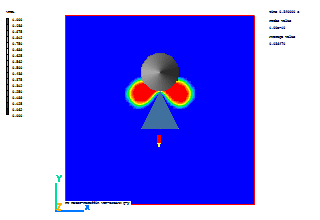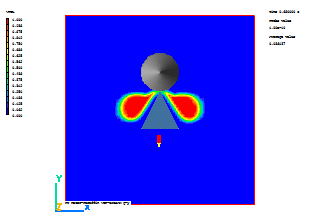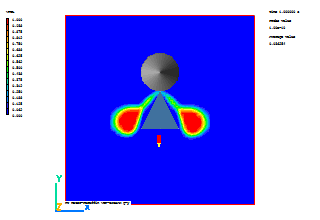
In the PHOENICS-VR environment, click on 'Run', 'Post processor',then GUI Post processor (VR Viewer) , and view the velocity vectors and contours of VFOL (Paraffin volume fraction).
A few selected plots at various time steps are shown below.
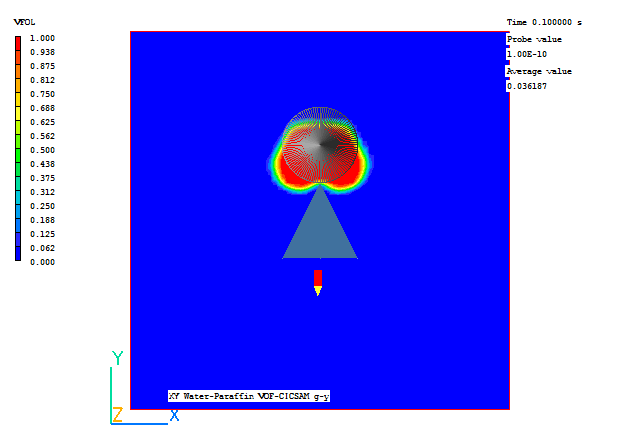 |
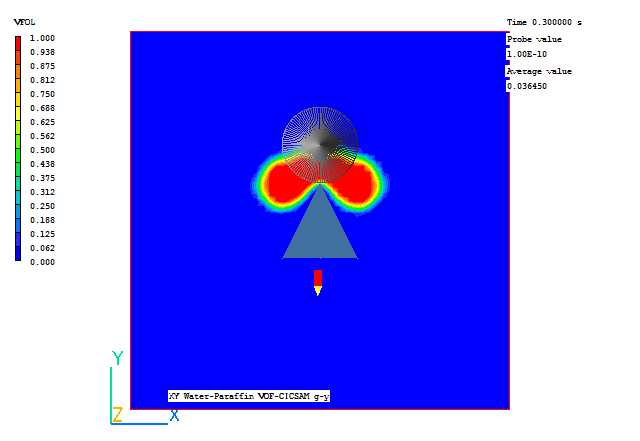 |
Time = 0.1 s |
Time = 0.3 s |
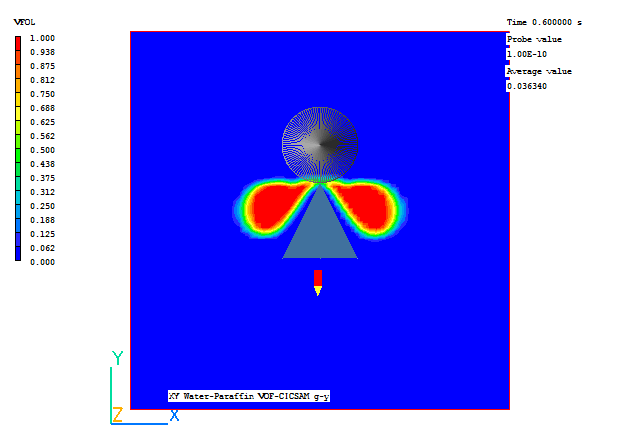 |
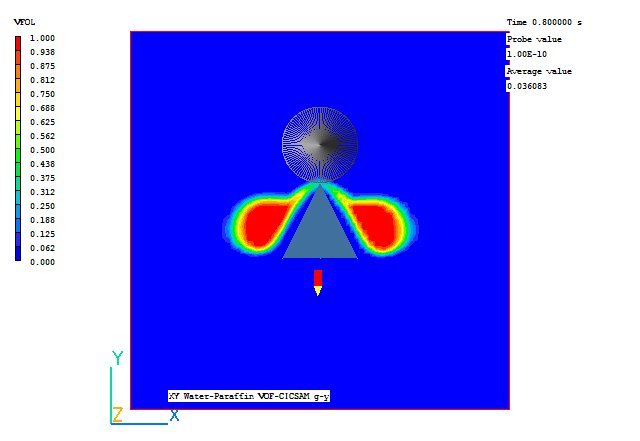 |
| Time = 0.6 | Time = 0.8 |
In the PHOENICS-VR environment, click on 'Save as a case', make a new folder called 'WEDGE' (e.g.) and save as 'CASE1' (e.g.).