Encyclopaedia Index
Title: IAHR Smooth Channel Test Case
By: S Semin - CHAM Development Team
Purpose of the Calculations:
- The problem considered is 2-dimensional, steady, laminar, isothermal flow in the
geometry devised by the IAHR Working Group on Refined Modeling of Flows. Results are
reported in the article "Laminar Flow in a Complex Geometry: A Comparison" in the
International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, Vol. 5, 667-683 (1985).
- The main objective of the calculations is to validate the Generalised Colocated Velocity
(GCV) solver.
- The solutions are compared with those of Cliffe et al., cited and used in the above
reference as a grid-independent benchmark.
Flow and Computational Details:
The main features of the problem are:
- Laminar flow, Re = 10.0
- The North and South boundaries of the channel are given by the following analytical
expression :
y(x) = +/- [tanh(2 - 30*x/Re) - tanh(2)]/2 for 0 ≤ x ≤ Re/3
- A parabolic profile for the axial velocity is specified at the inlet (shifted by -1 in
comparison to the IAHR reference),
u = (3/2)*(1 - y*y) for x = 0 and -1 ≤ y ≤ 1,
v = 0.
- A mesh of 64 cross-stream cells by 32 axial cells is used for a computational domain
length of Re/3.
This setup is available in PHOENICS' case library as Case B580.
The following images show:
The grid
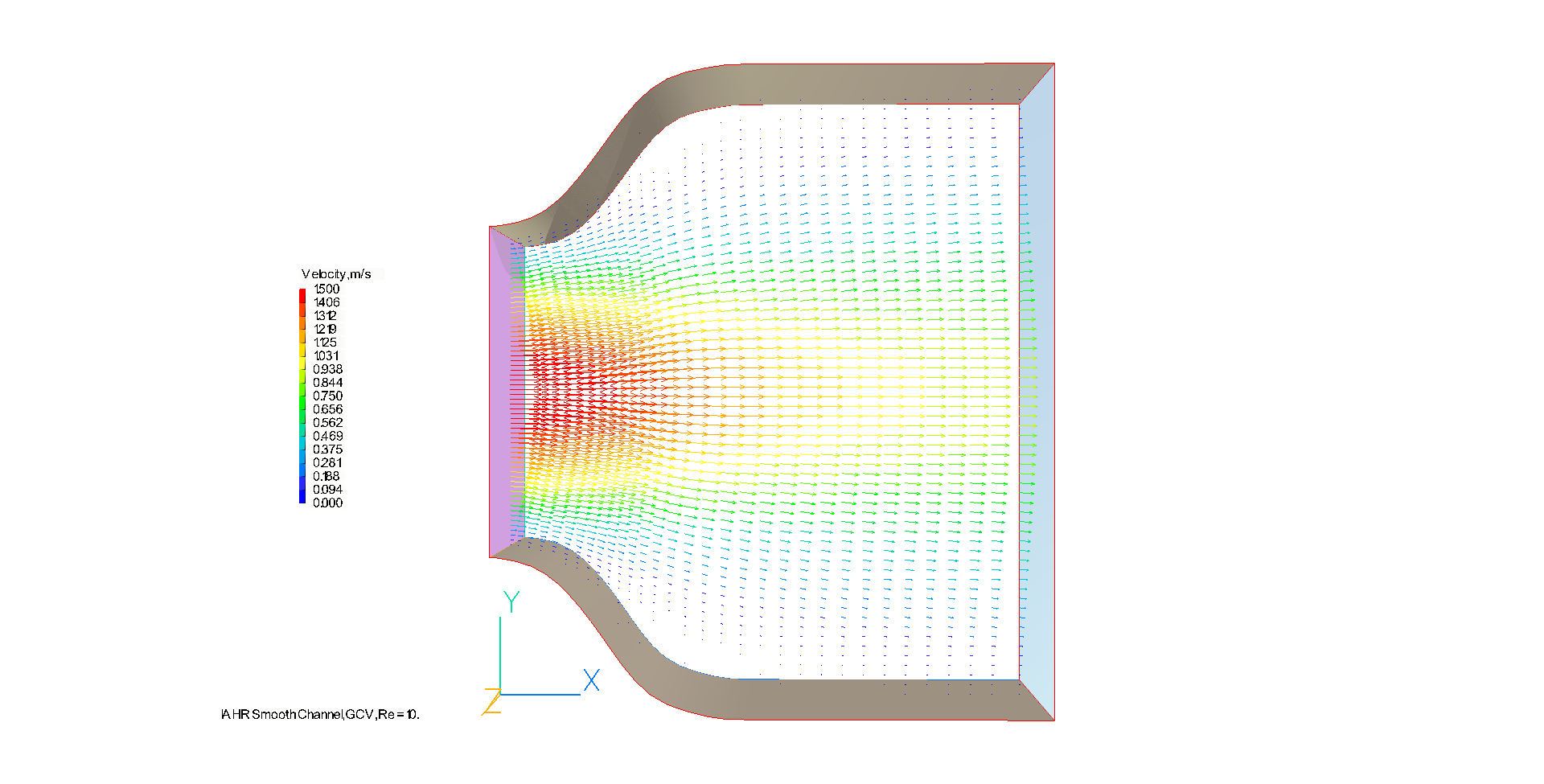
The velocity field
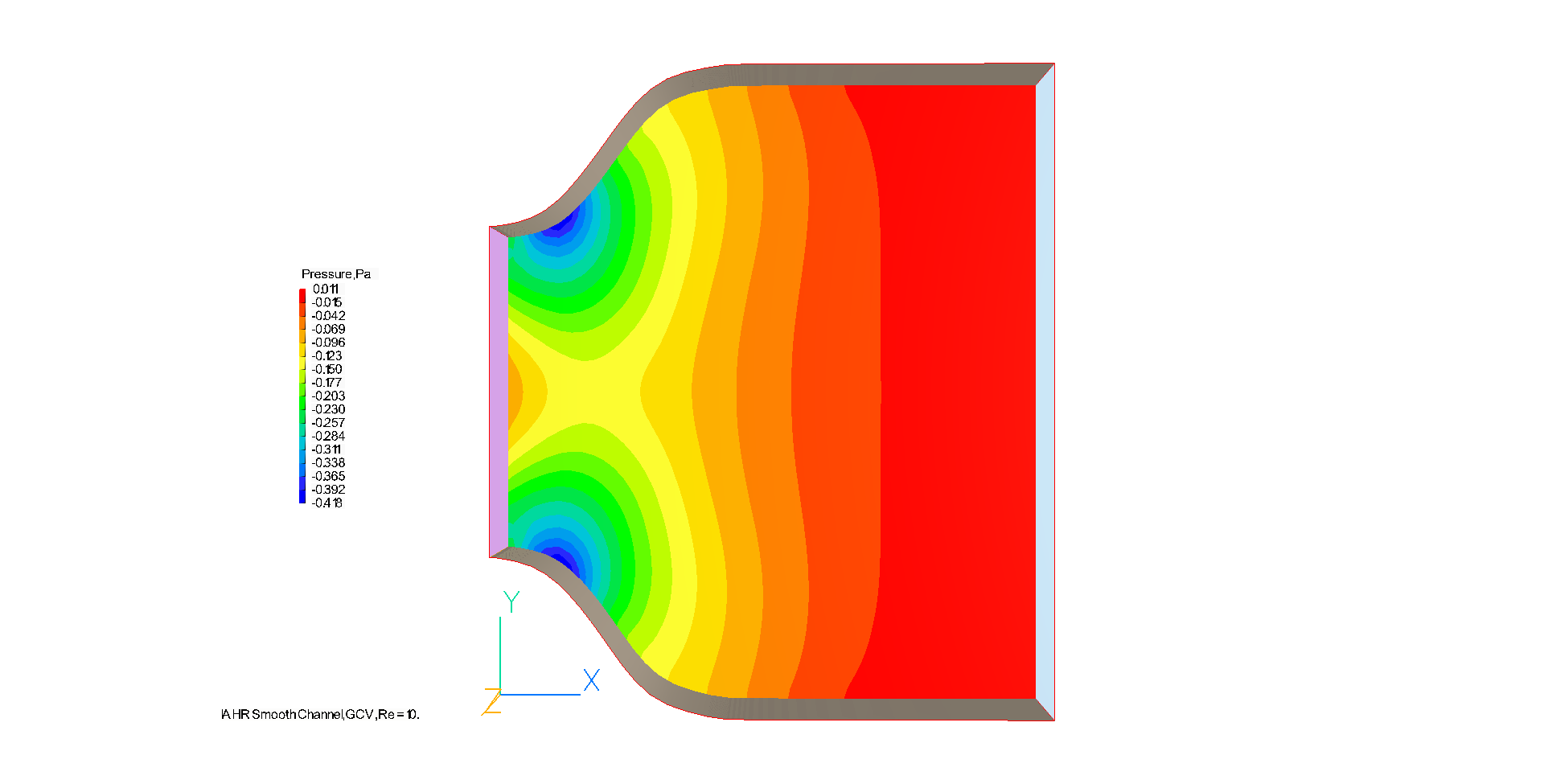
The pressure field
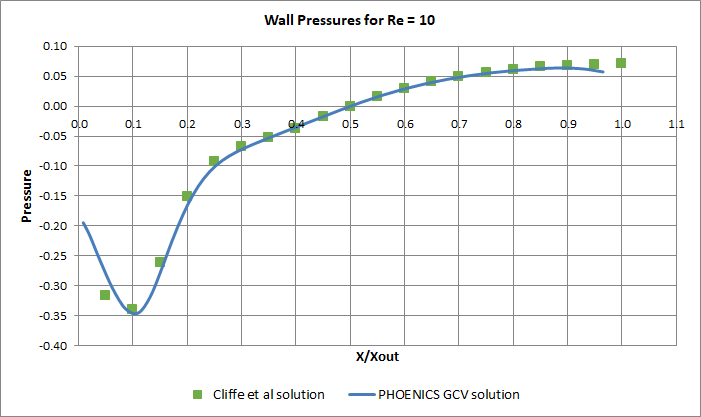
Comparison of surface pressure for Re = 10
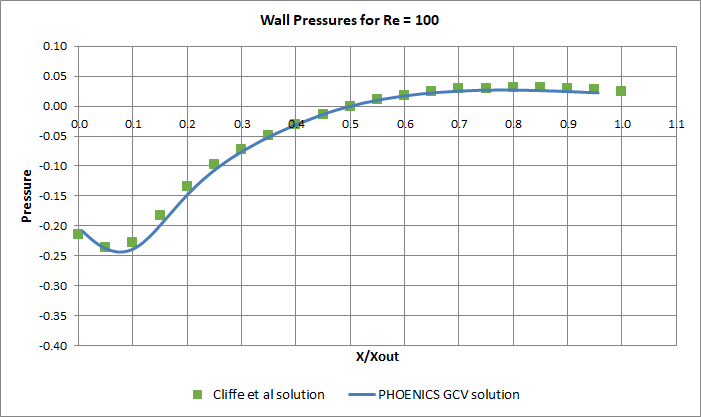
Comparison of surface pressure for Re = 100




